The Role of a Fleet Manager
Overview
A fleet manager oversees the daily operations of a fleet of vehicles, ensuring that they are utilized efficiently and maintained properly. This role is vital for companies that rely on transportation, whether for delivering goods, transporting passengers, or providing services.
Duties and Responsibilities
- Vehicle Acquisition: Fleet managers are responsible for acquiring new vehicles, ensuring that they meet the company’s needs and budget. This includes negotiating with suppliers and managing the purchase process.
- Fleet Maintenance: Regular maintenance is crucial to keep vehicles in good condition. Fleet managers must schedule and oversee preventative maintenance, handle repairs, and manage maintenance costs.
- Driver Management: Managing a fleet involves overseeing drivers, ensuring they are trained, compliant with regulations, and performing well. This includes setting driver schedules and monitoring driver behavior.
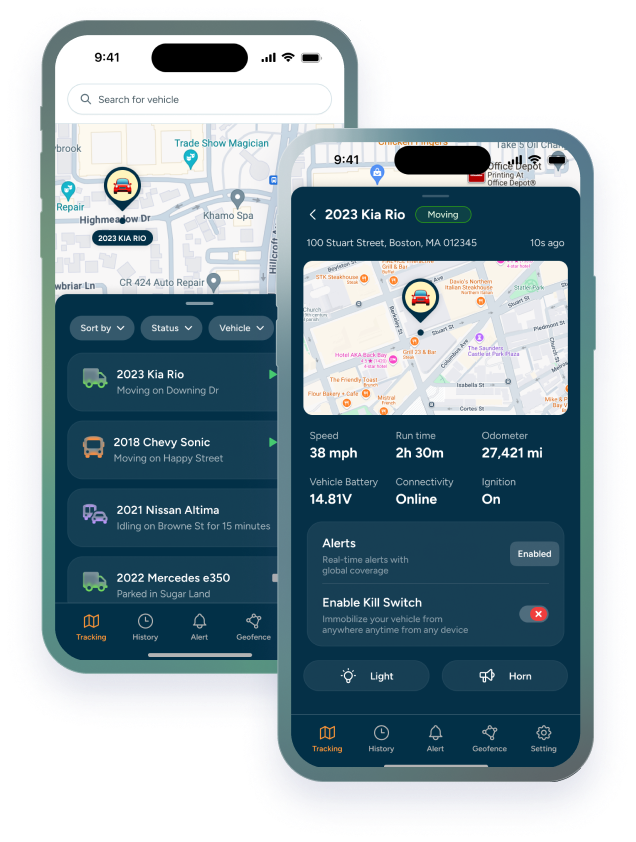
- Fleet Tracking: Using GPS tracking and fleet management software, fleet managers monitor the location and performance of vehicles in real-time. This helps in route planning and improving operational efficiency.
- Fuel Management: Fleet managers work to optimize fuel consumption and reduce fuel costs. This includes monitoring fuel efficiency and implementing strategies to improve it.
- Risk Management: Ensuring fleet safety and managing risks is a key responsibility. This involves implementing safety protocols, conducting regular safety training, and handling insurance and compliance issues.
- Operational Costs: Managing and reducing operational costs is essential. Fleet managers analyze costs related to vehicle maintenance, fuel, and driver management, and find ways to optimize expenses.
- Supply Chain Management: Fleet managers must coordinate with the supply chain to ensure timely deliveries and efficient transportation of goods.
- Driver Safety: Ensuring driver safety is a top priority. Fleet managers must implement and enforce safety regulations, conduct regular safety training programs, and monitor driver behavior to mitigate risks on the road.
- Customer Service: Maintaining a high level of customer service is crucial. Fleet managers work to ensure timely and reliable deliveries, which enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Importance of Fleet Management
Enhancing Efficiency
Efficient fleet management is critical for operational efficiency. By optimizing routes, maintaining vehicles, and managing drivers effectively, companies can ensure timely deliveries and reduce downtime.
Reducing Costs
Proper fleet management helps in controlling and reducing various costs, including fuel, maintenance, and operational expenses. This is essential for maintaining profitability and competitiveness.
Ensuring Safety
Driver safety and vehicle maintenance are paramount. Fleet managers implement safety protocols, monitor driver behavior, and ensure compliance with regulations to minimize accidents and enhance safety.
Improving Customer Service
Efficient fleet management leads to better customer service. Timely deliveries, reliable vehicles, and professional drivers contribute to a positive customer experience.
Environmental Impact
Fleet managers also play a role in reducing the environmental impact of transportation. By optimizing fuel consumption, implementing eco-friendly driving practices, and considering the use of electric or hybrid vehicles, they contribute to a more sustainable operation.
Tools and Techniques in Fleet Management
Fleet Management Software
Fleet management software is a critical tool that helps in tracking vehicles, managing maintenance schedules, monitoring driver performance, and analyzing data for decision-making. Features of fleet management software include:
- Real-Time Tracking: GPS tracking allows fleet managers to monitor the location of vehicles in real-time, enhancing route planning and efficiency.
- Maintenance Scheduling: Automated reminders for maintenance tasks help ensure vehicles are serviced on time, reducing breakdowns and repair costs.
- Driver Performance Monitoring: Tracking driver behavior, such as speed, braking, and idle time, helps in improving driver performance and safety.
- Fuel Management: Monitoring fuel consumption and identifying areas for improvement can lead to significant cost savings.
Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs)
ELDs are used to track hours of service (HOS) and ensure compliance with regulations. They help in monitoring driver schedules, reducing fatigue-related incidents, and improving overall safety.
Route Planning Tools
Advanced route planning tools help in optimizing routes, reducing travel time, and improving fuel efficiency. These tools consider factors such as traffic, weather, and road conditions.
Becoming a Fleet Manager
Education and Certification
To become a fleet manager, a bachelor’s degree in business, logistics, or a related field is often required. Certifications, such as Certified Automotive Fleet Specialist (CAFS) or Certified Automotive Fleet Manager (CAFM), can enhance career prospects.
Skills and Competencies
Fleet managers need strong analytical skills, attention to detail, and the ability to manage multiple tasks simultaneously. Good communication and leadership skills are also essential for managing drivers and coordinating with other departments.
Experience
Experience in the transportation or logistics industry is valuable. Many fleet managers start in entry-level positions and work their way up, gaining knowledge and expertise in fleet operations.
Fleet Management Best Practices
Implement Preventative Maintenance
Regular preventative maintenance is essential to keep vehicles running smoothly and reduce unexpected breakdowns. This includes regular inspections, oil changes, and tire rotations.
Monitor Driver Behavior
Using telematics and GPS tracking, fleet managers can monitor driver behavior and provide feedback or training to improve performance. This includes addressing issues such as speeding, harsh braking, and excessive idling.
Optimize Fuel Usage
Implementing fuel management strategies, such as monitoring fuel consumption and optimizing routes, can lead to significant cost savings. Encourage drivers to adopt fuel-efficient driving practices.
Utilize Fleet Management Software
Investing in fleet management software can streamline operations, reduce administrative tasks, and provide valuable insights for decision-making. Choose software that integrates well with your existing systems and meets your specific needs.
Train and Educate Drivers
Regular training programs for drivers are crucial for maintaining safety and efficiency. This includes training on safe driving practices, vehicle maintenance, and the use of electronic logging devices.
Regularly Review and Update Policies
Fleet managers must regularly review and update policies to reflect changes in regulations, industry standards, and company objectives. This ensures that the fleet operates within legal requirements and aligns with organizational goals.
The Future of Fleet Management
The fleet management industry is continuously evolving, with new technologies and trends shaping the way fleet managers operate. Here are some emerging trends:
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The adoption of electric vehicles is on the rise, driven by the need for sustainability and reducing fuel costs. Fleet managers must adapt to managing EVs, including charging infrastructure and maintenance.
Advanced Telematics
Telematics technology is becoming more advanced, offering deeper insights into vehicle performance, driver behavior, and operational efficiency. This technology will play a crucial role in the future of fleet management.
Automation and AI
Automation and artificial intelligence are set to revolutionize fleet management. From automated route planning to predictive maintenance, these technologies can significantly enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
Data Analytics
The use of data analytics in fleet management is increasing, allowing managers to make data-driven decisions. Analyzing data from various sources helps in identifying trends, improving operational efficiency, and reducing costs.
Case Studies and Customer Stories
Small Business Success
Consider a small delivery business that implemented fleet management software and saw a significant reduction in fuel costs and improved driver performance. By optimizing routes and monitoring driver behavior, the company achieved greater operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Large-Scale Fleet Management
A large logistics company in the United States adopted advanced telematics and GPS tracking to manage its extensive fleet of commercial vehicles. The result was improved fuel efficiency, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced fleet safety.
Conclusion
A fleet manager plays a pivotal role in the efficient operation of a company’s fleet of vehicles. From managing vehicle acquisition and maintenance to overseeing drivers and optimizing fuel usage, the responsibilities are vast and varied. With the right tools, such as fleet management software and GPS tracking, fleet managers can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure safety. As the industry evolves, staying updated with new technologies and best practices will be essential for continued success in fleet management.
Understanding the role of a fleet manager and the importance of effective fleet management can help businesses improve their operations and achieve their goals. Whether you’re looking to become a fleet manager or enhance your current fleet management practices, the insights and strategies discussed in this article will guide you towards success.